What is Atrial Flutter?
Quick Facts
- Atrial flutter is a kind of abnormal heart rhythm.
- It happens when the heart’s upper chambers beat faster than normal and aren’t coordinated.
- Treatment options include medication and ablation.
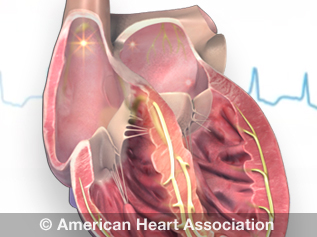
Atrial flutter is a rhythmic disturbance of the heart (arrhythmia). Atrial flutter happens when the chambers beat faster than normal and are not always coordinated. It is not as common as atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib or AF. But atrial flutter has similar symptoms, causes and results. People with atrial flutter may also develop AFib. An electrocardiogram can detect atrial flutter.
During atrial flutter, the upper chambers of the heart, also called the atria, beat 250 to 350 times per minute. With atrial flutter, the signal that tells the atrium to beat may be blocked by damaged tissue or scar tissue.
Watch an animation of a normal heartbeat.
Symptoms of atrial flutter
Sometimes, there are no obvious symptoms, and the condition is found only with a physical exam. When there are obvious symptoms, they may include:
- General fatigue
- A rapid and irregular heartbeat
- Fluttering or “thumping” in the chest
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety
- Weakness
- Faintness or confusion
- Fatigue when exercising
- Sweating
- Chest pain or pressure (If you have this or any other concerning symptom, this is a medical emergency. You may be having a heart attack. Call 911 right away.)
What causes atrial flutter?
The cause of atrial flutter may be unknown. In some cases, it is the result of damage to the heart’s electrical system. This may be caused by other conditions such as:
- Long-term, uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart valve disorders
- Birth defects of the heart
- Alcohol abuse
- Overactive thyroid gland
The most serious risk from atrial flutter is that it can lead to other medical problems, including:
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Chronic fatigue
- Additional heart rhythm problems
- Inconsistent blood supply to the body
What are the risk factors for atrial flutter?
- High blood pressure
- Older age
- Diabetes
- History of alcohol use
Treatment for atrial flutter
The treatment for atrial flutter is like the treatment for AFib. The goals of treatment include:
- Slowing the heart rate with medication
- Restoring the normal heart rhythm with cardioversion, medications or ablation
- Preventing blood clots