All in the family: 3 generations take on the same defective heart valve
By Katherine Shaver, American Heart Association News
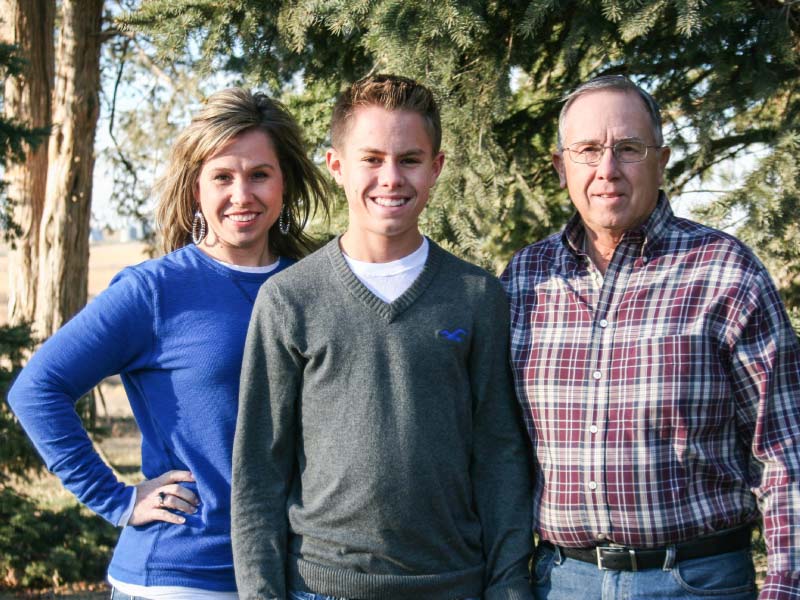

Around the time a cardiologist diagnosed Keri Mathew with a heart problem at age 4, her dad once again failed the physical required to increase his life insurance policy.
So Gary Peterson went to see that cardiologist, too.
Mathew, who grew up in southwest Iowa, had been born with a heart murmur that might eventually correct itself. When it was still there at her pre-kindergarten physical, she went to cardiologist Dr. Ward A. Chambers of Omaha, Nebraska, for more tests.
Chambers found that Mathew was born with a bicuspid aortic valve, meaning the aortic valve in her heart had two flaps rather than the normal three; this allowed blood to leak backward into her heart instead of getting fully pumped into the aorta and to the rest of her body. Even back then, in the late 1970s, the problem was considered manageable, although Chambers warned that Mathew might eventually need the valve replaced.
Peterson also had been told he had a heart murmur. He'd learned that in high school. By the time he met Chambers, he was in his early 30s. He'd never had any trouble with his heart, so he hadn't looked into the murmur before his daughter's diagnosis. Chambers found that Peterson also had a bicuspid aortic valve. Also like his daughter, Peterson was told to wait and see about any treatment.
To Peterson, the devastating part of the diagnosis was "that I had passed it on."
Six years later, Peterson was hospitalized for a bacterial infection in his heart. Once back home on his farm, he began getting tired more easily as he ran the combine and cared for his livestock.
"I just didn't have the stamina," he said.
At 39, he had open-heart surgery to replace his defective valve with a mechanical one. Mathew, who was 10 at the time, worried for her dad and knew it "was what I was going to face one day."
By middle school, she began to get winded easily. She avoided athletics, never playing on teams or even running laps in PE class. She wished she could be like other kids, doing everything they could do.
By college, singing in the show choir left Mathew short of breath.
At 29, simply vacuuming or walking between her car and office left her gasping for air. Now living in the Kansas City, Missouri, area, her local cardiologist recommended a new aortic valve.
"I'd put it off as long as I could," she said.
Like her father, Mathew got a mechanical valve. Her surgeon also reinforced a damaged part of her aorta.
By this point, a third generation of the family had been diagnosed with a bicuspid aortic valve: Dakota Mathew, Keri's first child.
Keri and her husband, Kip Mathew, knew that could happen. Sure enough, doctors heard a heart murmur in Dakota as a newborn and diagnosed the congenital heart defect at 6 months old.
Given all the knowledge and experience from her own case and her dad's, Keri thought it "was probably something that we could handle."
A few years later, Keri gave birth again, to a daughter named Riley. Her heart turned out normal.
Then, when Peterson was 62, he endured more heart problems. He underwent a second open-heart surgery, this time to bypass two clogged arteries and repair an aneurysm in his aorta. A few years later, after he became winded climbing the 18-foot ladder to the top of the grain bins on his farm, he also got a pacemaker.
Along the way, Keri faced new challenges, too.
Her heart began beating irregularly, sometimes abnormally slowly. She received a pacemaker to regulate her heartbeat. Three years later, during an especially stressful time, she had a mini-stroke; it left no lasting effects.
Through it all, Dakota hardly thought about his defective valve beyond occasionally wondering when he would need the same open-heart surgery as his mother and grandfather. Although he ran out of breath more quickly than other kids, he was healthy enough to play competitive soccer and sing in a choir.
Dakota grew up in the Kansas City area, then attended the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Chambers was still seeing patients, including Peterson, at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. Chambers began seeing Dakota as well.
"To see a bicuspid valve that leaks – sure, that happens," said Chambers, a professor of medicine and public health. "But to have it in three generations? I've seen a lot of bicuspid valves in my 47-year career, but I'd never seen it in three generations like that."
Dakota was 24 when Chambers said it was time to replace the faulty valve and part of his aorta.
Dakota was nervous, of course. However, "it eased my mind a little bit that there were two people that had it and got on with a normal life afterward," he said.
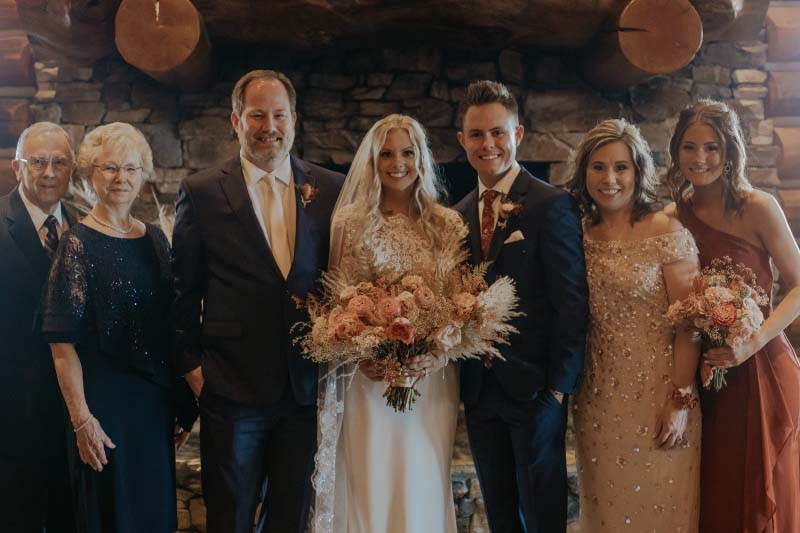
Now, two years later, Dakota is a high school choir teacher in a suburb of Omaha. Like his mother and grandfather, he said he's grateful for Chambers and the care team. He also feels lucky that their heart problem could be fixed.
That's why, he said, he doesn't worry if he and his wife, McKenna, someday have a child with the same defect.
"I know with the medical advancements that have been made, my kid will be OK if they have it," Dakota said. "It's been proven three different times now with the three of us that the medical field is amazing."
Stories From the Heart chronicles the inspiring journeys of heart disease and stroke survivors, caregivers and advocates.





